Select all the statements that are true regarding enzymes. Enzymes are essential for life, and they play a vital role in a wide range of cellular processes. They are responsible for catalyzing chemical reactions, which are the processes that allow cells to function.
Without enzymes, these reactions would occur too slowly to sustain life.
In this article, we will discuss the different types of enzymes, their structure and function, and their importance in cellular metabolism. We will also explore some of the applications of enzymes in industry and medicine.
Enzymes as Catalysts
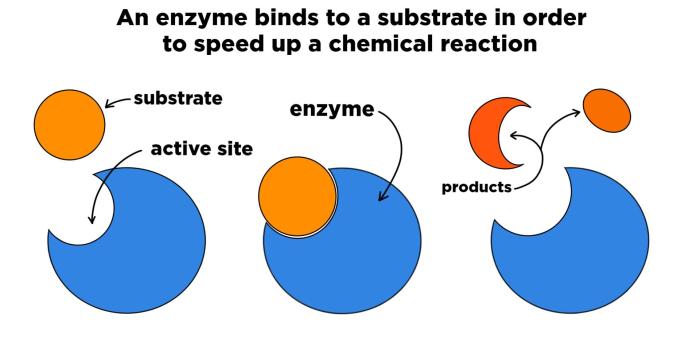
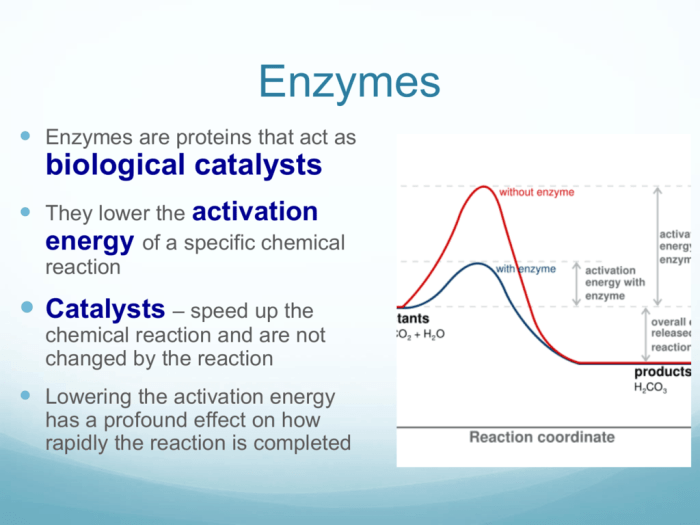
Enzymes are biological molecules that act as catalysts in chemical reactions, facilitating the conversion of reactants to products without being consumed in the process. They increase the rate of reactions by providing an alternative pathway with a lower activation energy, enabling reactions to occur more rapidly at physiological temperatures.
Enzymes are highly specific, each catalyzing a particular reaction or a group of related reactions.
Examples of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions, Select all the statements that are true regarding enzymes.
-
-*Digestion
Enzymes such as proteases and lipases break down proteins and fats into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body.
-*Metabolism
Enzymes catalyze the breakdown of glucose and other nutrients to produce energy.
-*DNA replication
Enzymes such as DNA polymerase and ligase are essential for the replication of genetic material.
Enzyme Structure and Function
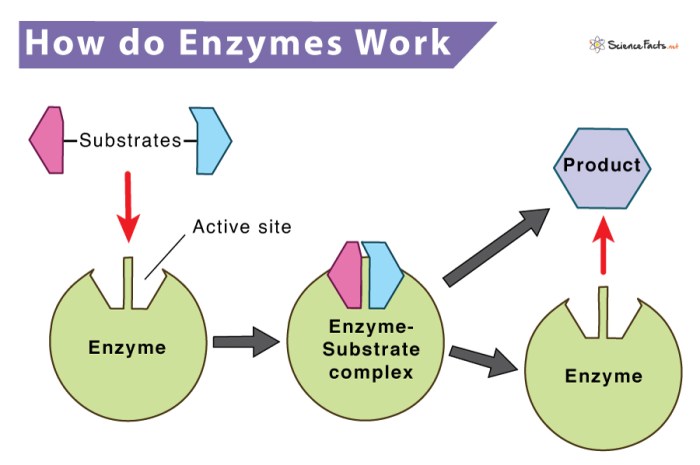
Enzymes are typically proteins with a specific three-dimensional structure. The active site is the region of the enzyme that binds to the substrate, the molecule that is being converted. Cofactors, such as metal ions or organic molecules, may be required for enzyme activity.The
structure of an enzyme determines its specificity and efficiency. The active site is designed to bind to a specific substrate or group of substrates, excluding others. The shape and chemical properties of the active site complement the substrate, allowing for optimal interactions and catalysis.
Enzyme Kinetics: Select All The Statements That Are True Regarding Enzymes.
Enzyme kinetics studies the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions and the factors that influence it. The Michaelis-Menten equation is a mathematical model that describes the relationship between the substrate concentration and the reaction rate. It allows for the determination of kinetic parameters such as the Michaelis constant (Km) and the maximum reaction rate (Vmax).Enzyme
kinetics experiments can provide insights into enzyme mechanisms, substrate specificity, and the effects of inhibitors and activators.
Enzyme Inhibition
Enzyme inhibitors are molecules that bind to enzymes and reduce their activity. They can be classified as competitive, non-competitive, or uncompetitive inhibitors. Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site and compete with the substrate for binding, while non-competitive inhibitors bind to a different site on the enzyme and alter its conformation.
Uncompetitive inhibitors bind to an enzyme-substrate complex, preventing the release of the product.Enzyme inhibition is important in drug development, as many drugs target enzymes to inhibit their activity and treat various diseases.
Enzyme Regulation
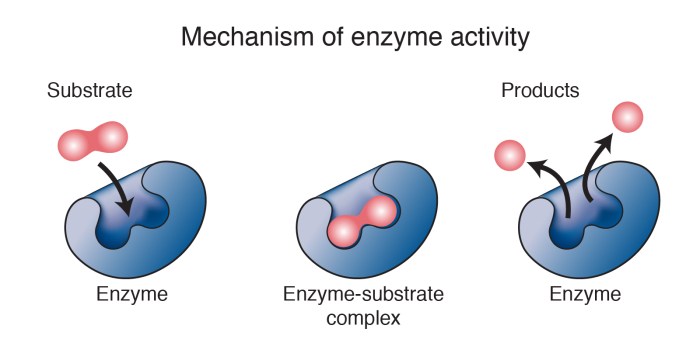
Enzyme activity is regulated by various mechanisms to ensure cellular homeostasis. Feedback inhibition occurs when the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits the enzyme that catalyzes its synthesis. Allosteric regulation involves the binding of small molecules to an allosteric site on the enzyme, which can either activate or inhibit its activity.Enzyme
regulation is essential for coordinating metabolic pathways, responding to changes in cellular conditions, and maintaining cellular balance.
Applications of Enzymes
Enzymes have numerous industrial applications, including in food processing, biotechnology, and pharmaceuticals. In food processing, enzymes are used to modify the texture, flavor, and nutritional value of food products. In biotechnology, enzymes are employed in the production of biofuels, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
In medicine, enzymes are used in diagnostics and therapeutics, such as enzyme replacement therapy for genetic disorders.
FAQ Guide
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions.
How do enzymes work?
Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy of a reaction. This means that they make it easier for the reaction to occur.
Are enzymes specific?
Yes, enzymes are specific for the reactions that they catalyze.
What are some examples of enzymes?
Some examples of enzymes include amylase, which breaks down starch, and protease, which breaks down proteins.