Figure animations comparison of action potentials and graded potentials embarks on a captivating journey into the realm of electrical signals that govern life’s processes. Action potentials and graded potentials, the fundamental units of neural communication, orchestrate a symphony of physiological events, from nerve impulse transmission to muscle contraction.
This exploration unveils the intricate differences between these electrical signals, their generation and propagation mechanisms, and their vital roles in biological systems. Through a series of visually stunning animations, we delve into the temporal and spatial dynamics of these electrical impulses, illuminating their significance in neuroscience, medicine, and beyond.
Comparison of Action Potentials and Graded Potentials: Figure Animations Comparison Of Action Potentials And Graded Potentials
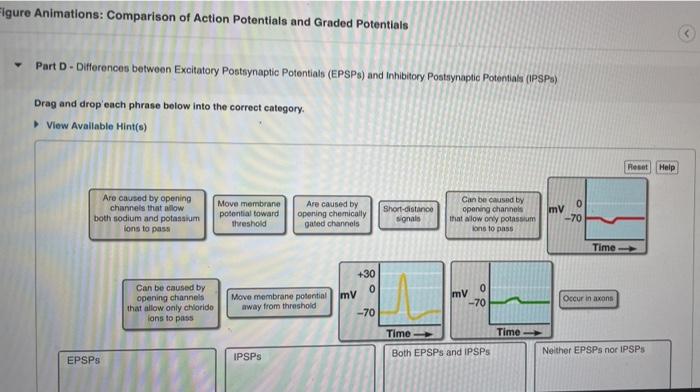
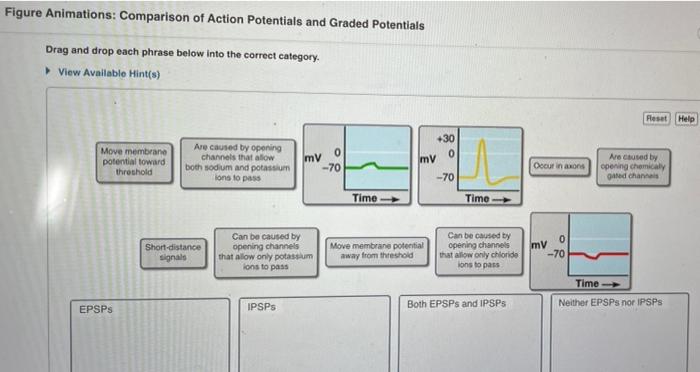
Action potentials and graded potentials are two distinct types of electrical signals that transmit information within biological systems. Action potentials are brief, all-or-nothing electrical impulses that propagate along the length of a neuron, while graded potentials are graded changes in the electrical potential of a cell that vary in amplitude and duration.
Key Characteristics, Figure animations comparison of action potentials and graded potentials
The key characteristics of action potentials and graded potentials are summarized in the following table:
| Characteristic | Action Potentials | Graded Potentials |
|---|---|---|
| Threshold | Yes | No |
| Duration | Brief (1-2 milliseconds) | Varies (can last several seconds) |
| Propagation | Propagates along the axon | Decays over distance |
| Refractory Period | Yes | No |
Role of Ion Channels
Action potentials and graded potentials are generated and propagated by the opening and closing of ion channels in the cell membrane. Ion channels are pores that allow ions to flow across the membrane, changing the electrical potential of the cell.
The opening of sodium channels triggers an action potential, while the opening of potassium and chloride channels contributes to the generation and propagation of graded potentials.
Figure Animations
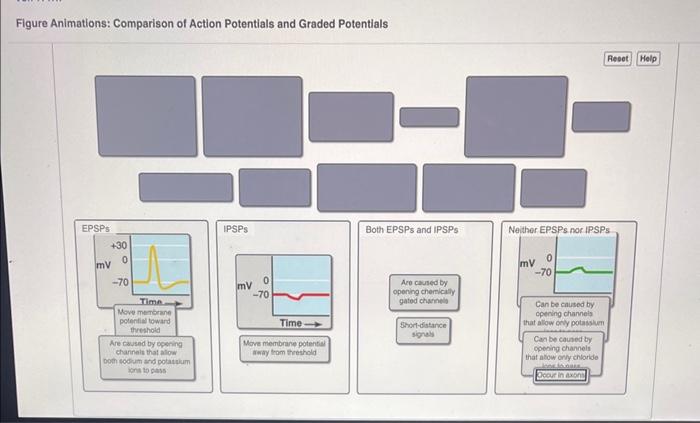
The following animated figures visually demonstrate the generation and propagation of action potentials and graded potentials:
- Figure 1: Generation of an Action Potential
- Figure 2: Propagation of an Action Potential
- Figure 3: Generation of a Graded Potential
- Figure 4: Propagation of a Graded Potential
These animations accurately represent the temporal and spatial aspects of these electrical signals, including the opening and closing of ion channels, the flow of ions across the membrane, and the changes in electrical potential.
Examples and Applications
Action potentials and graded potentials are used in a variety of biological systems, including:
- Nerve impulse transmission: Action potentials transmit information from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord, and from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands.
- Muscle contraction: Action potentials trigger the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which leads to the contraction of muscle fibers.
- Sensory transduction: Graded potentials are used to encode sensory information, such as touch, temperature, and pain.
Understanding action potentials and graded potentials has important applications in fields such as neuroscience, medicine, and biotechnology, including the development of new drugs and therapies for neurological disorders.
FAQ Guide
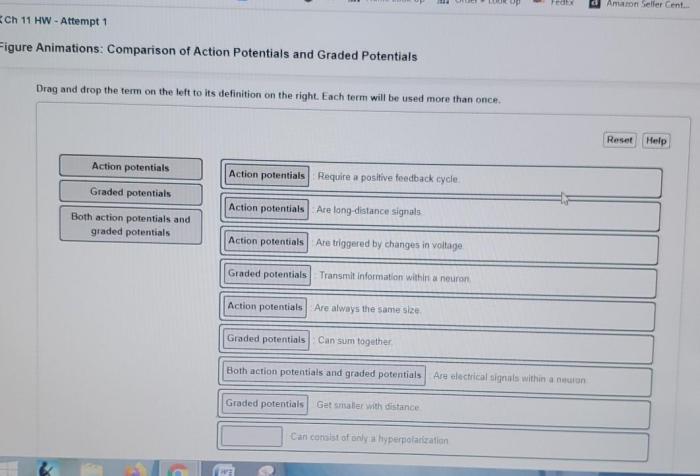
What are the key differences between action potentials and graded potentials?
Action potentials are all-or-nothing signals that exhibit a threshold, while graded potentials vary in amplitude depending on the strength of the stimulus.
How are action potentials and graded potentials generated?
Action potentials are generated by the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels, while graded potentials are generated by the opening of ligand-gated ion channels.
What are the applications of understanding action potentials and graded potentials?
Understanding action potentials and graded potentials has applications in neuroscience, medicine, and biotechnology, including the development of new drugs and therapies.