Exercise 31 conduction system of the heart and electrocardiography – Exercise 31: Conduction System of the Heart and Electrocardiography embarks on an illuminating exploration of the electrical pathways that orchestrate the heartbeat and the invaluable tool used to decipher these signals, the electrocardiogram (ECG). This comprehensive study unveils the intricate mechanisms underlying cardiac function, empowering healthcare professionals with the knowledge to diagnose and manage a wide spectrum of cardiac conditions.
The electrical impulses that govern the rhythmic contractions of the heart originate from specialized cells within the conduction system, beginning with the sinoatrial (SA) node. The atrioventricular (AV) node serves as a gatekeeper, delaying these impulses to allow for proper filling of the ventricles.
Within the ventricles, the bundle of His and Purkinje fibers distribute the electrical signals, ensuring synchronized contraction of the heart’s chambers.
Conduction System of the Heart: Exercise 31 Conduction System Of The Heart And Electrocardiography
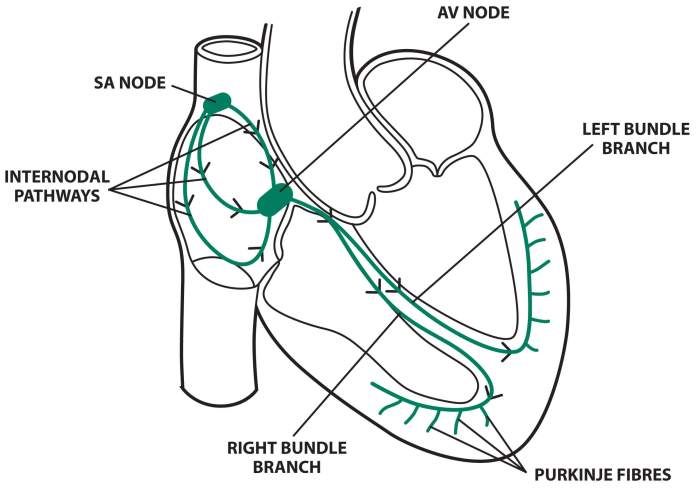
The conduction system of the heart is a specialized network of cells that generates and conducts electrical impulses, coordinating the rhythmic contraction of the heart muscle. It consists of:
- Sinoatrial (SA) node:Located in the right atrium, the SA node is the natural pacemaker of the heart, generating electrical impulses that initiate each heartbeat.
- Atrioventricular (AV) node:Located between the atria and ventricles, the AV node delays electrical impulses, allowing the atria to fill with blood before the ventricles contract.
- Bundle of His:A bundle of fibers that transmits electrical impulses from the AV node to the ventricles.
- Purkinje fibers:A network of fibers that distribute electrical impulses throughout the ventricles, ensuring coordinated contraction.
Electrocardiography (ECG)
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a non-invasive technique that records the electrical activity of the heart. It is used to diagnose a wide range of cardiac conditions.
- ECG waveform:The ECG waveform consists of several components, including the P wave (atrial depolarization), QRS complex (ventricular depolarization), and T wave (ventricular repolarization).
- ECG interpretation:ECGs can be used to diagnose arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms), myocardial infarction (heart attack), and other cardiac conditions.
ECG Analysis

ECG analysis involves interpreting the ECG waveform to assess cardiac function.
- Arrhythmia diagnosis:ECGs can be used to diagnose various arrhythmias, such as sinus tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and ventricular tachycardia.
- Cardiac function evaluation:ECGs can be used to evaluate heart rate, rhythm, and conduction abnormalities.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the sinoatrial (SA) node?
The SA node is a group of specialized cells located in the right atrium that initiates the electrical impulses that trigger the heartbeat.
What is the role of the atrioventricular (AV) node?
The AV node delays the electrical impulses from the SA node, allowing the atria to fill completely before the ventricles contract.
What is the bundle of His?
The bundle of His is a group of fibers that conducts the electrical impulses from the AV node to the ventricles.
What is an electrocardiogram (ECG)?
An ECG is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart, providing valuable information about heart rate, rhythm, and any abnormalities.