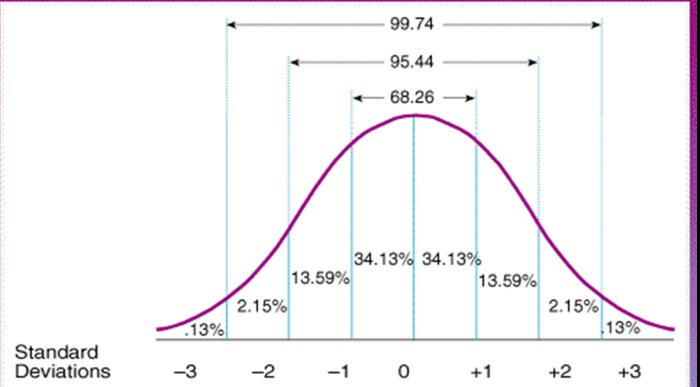
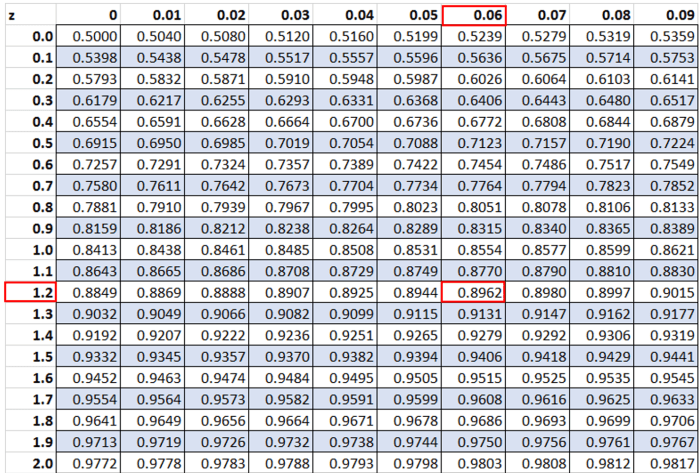
Find the standard normal area for each of the following: Embark on a journey into the realm of probability and statistics, where we delve into the intricacies of the standard normal distribution. This essential tool provides a foundation for understanding countless real-world phenomena, from predicting election outcomes to evaluating medical test results.
As we unravel the mysteries of the standard normal curve, we will explore its unique properties, learn how to calculate standard normal areas, and uncover the practical applications that make it an indispensable tool for researchers and practitioners alike.
Standard Normal Distribution: Find The Standard Normal Area For Each Of The Following
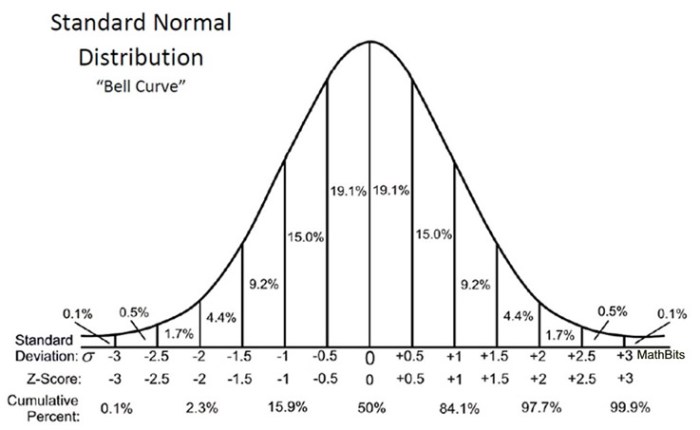
The standard normal distribution, also known as the Gaussian distribution or bell curve, is a continuous probability distribution that describes the distribution of a random variable with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. It is a symmetrical distribution, meaning that the left and right halves of the curve are mirror images of each other.
The standard normal distribution is often used to model real-world phenomena, such as the distribution of heights or weights in a population. The formula for the standard normal distribution is:$$f(z) = \frac1\sqrt2\pi e^-\fracz^22$$where:
- $f(z)$ is the probability density function of the standard normal distribution
- $z$ is the z-score, which is the number of standard deviations a given value is away from the mean
A table or graph of the standard normal distribution can be used to find the area under the curve between any two z-scores.
Finding Standard Normal Areas, Find the standard normal area for each of the following
The area under the standard normal curve between any two z-scores can be found using a table or formula. The formula for the area under the standard normal curve is:$$P(a < Z < b) = \Phi(b) - \Phi(a)$$ where: - $P(a < Z < b)$ is the area under the standard normal curve between z-scores $a$ and $b$ - $\Phi(a)$ is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution at z-score $a$ - $\Phi(b)$ is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution at z-score $b$ A table of the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution can be found in most statistics textbooks. A calculator or software can also be used to find standard normal areas.
Examples of Finding Standard Normal Areas
For example, to find the area under the standard normal curve between z-scores
-1 and 1, we can use the formula
$$P(-1 < Z < 1) = \Phi(1) - \Phi(-1) = 0.6827 - 0.1587 = 0.524$$ This means that 52.4% of the area under the standard normal curve is between z-scores -1 and 1.
Applications of Standard Normal Areas
Standard normal areas are used in a variety of statistical and probability applications, including:* Hypothesis testing
- Confidence intervals
- Power analysis
- Sampling distributions
Standard normal areas can also be used to model real-world phenomena, such as the distribution of heights or weights in a population.
Quick FAQs
What is the standard normal distribution?
The standard normal distribution is a bell-shaped probability distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. It is often used to model continuous random variables.
How do I find the standard normal area for a given z-score?
You can use a standard normal table or calculator to find the standard normal area for a given z-score. The area to the left of a positive z-score represents the probability that a randomly selected value from a standard normal distribution will be less than that z-score.
What are some applications of the standard normal distribution?
The standard normal distribution is used in a wide variety of applications, including hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis.