The Compound Fracture HESI Case Study embarks on an in-depth exploration of the multifaceted nature of compound fractures, their impact on patient care, and the comprehensive strategies employed in their management. This case study delves into the intricacies of assessment, diagnosis, treatment planning, nursing interventions, potential complications, and prognosis, providing a comprehensive understanding of this critical topic.
Compound Fractures: Case Study Overview: Compound Fracture Hesi Case Study
Compound fractures, also known as open fractures, are a serious type of injury that occurs when a bone breaks and protrudes through the skin. They pose significant challenges in patient care due to the risk of infection, delayed healing, and functional impairment.
Case Study:
- Patient: 25-year-old male
- Mechanism of injury: Motor vehicle accident
- Initial presentation: Deformity, swelling, and open wound on the left tibia
Assessment and Diagnosis

Clinical Assessment:
- Physical examination: Inspect wound for size, depth, and presence of bone fragments
- Neurovascular assessment: Check sensation, motor function, and capillary refill
Diagnostic Procedures:
- X-rays: Determine fracture pattern and extent
- Computed tomography (CT) scan: Provide detailed images of bone and soft tissue damage
Signs and Symptoms:
- Deformity and swelling
- Open wound with visible bone fragments
- Pain, tenderness, and crepitus
- Neurovascular compromise (in severe cases)
Treatment Plan
Principles of Treatment:
- Stabilize fracture
- Clean and debride wound
- Prevent infection
- Promote healing
Surgical Techniques:
- Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF): Surgery to align and stabilize bone fragments with screws, plates, or rods
- External fixation: Surgery to stabilize bone fragments with pins and an external frame
Antibiotic Therapy:
- Prophylactic antibiotics to prevent infection
- Therapeutic antibiotics to treat established infection
- Common antibiotics used: Cefazolin, Vancomycin, Clindamycin
Nursing Management
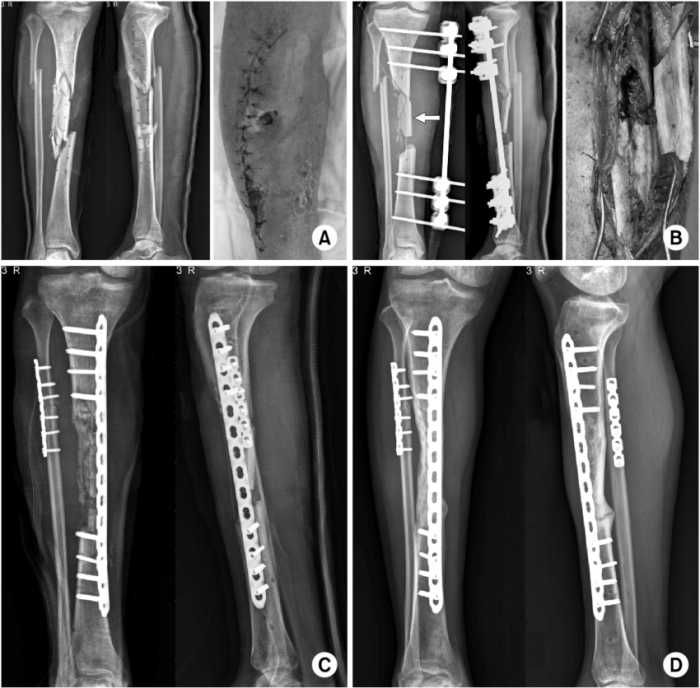
Essential Interventions:
- Pain management
- Wound care: Cleaning, dressing, and monitoring for infection
- Infection prevention: Antibiotics, sterile technique, and isolation
- Patient education and support: Explain care plan, provide emotional support
Nursing Care Plans and Protocols:
- Compound Fracture Care Plan
- Wound Management Protocol
- Infection Prevention Protocol
Complications and Prognosis
Potential Complications:
- Infection: Osteomyelitis, septic arthritis
- Non-union: Failure of fracture to heal
- Malunion: Fracture heals in an abnormal position
Factors Influencing Prognosis:
- Severity of injury
- Patient’s overall health
- Timeliness of treatment
Rehabilitation:
- Physical therapy to restore range of motion and strength
- Occupational therapy to improve functional skills
- Psychological support to address emotional impact
Case Study Discussion
Key Assessment Findings:
- Open wound on left tibia with protruding bone fragments
- Swelling, deformity, and crepitus
- Neurovascular compromise
Treatment Decisions:
- ORIF surgery to stabilize fracture
- Antibiotic therapy to prevent infection
Nursing Interventions:
- Wound care and infection prevention
- Pain management
- Patient education and support
Areas for Improvement:
- Earlier antibiotic administration
- More frequent wound monitoring
- Improved pain management protocol
Ethical Considerations:
- Informed consent for surgery
- Pain management and patient comfort
- End-of-life care decisions
Question Bank
What is the significance of compound fractures?
Compound fractures are severe injuries that involve an open wound, exposing the bone to the external environment. They pose significant risks of infection, delayed healing, and potential complications, requiring prompt and specialized medical attention.
How are compound fractures diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a comprehensive assessment, including physical examination, imaging studies (X-rays, CT scans), and laboratory tests to evaluate the extent of injury, identify potential complications, and guide treatment decisions.
What are the principles of treatment for compound fractures?
Treatment aims to stabilize the fracture, manage the wound, prevent infection, and promote healing. Surgical intervention is often necessary to align and fixate the bone fragments, while antibiotics are administered to combat infection. Wound care plays a crucial role in preventing further contamination and promoting tissue repair.
